Adoption of Business Intelligence and Big Data Analytics for business
A guide on how businesses can get started with Business Intelligence and benefit from it and subsequently accelerate Big Data Analytics adoption.
What are Big Data Analytics and its benefits?
Big data analytics is a process that uses technology and advanced analysis techniques to analyse large sets of data to extract valuable findings and insights. It focuses on exploring a large volume of data to find correlations and trends. This technology has empowered businesses to uncover hidden trends, improve workflow and operational efficiency and garner the highest returns for their marketing effort by utilising predictive and big data analytics, including enhancing business intelligence.
The attributes of big data analytics include velocity, volume, value, veracity, and variety (Tran, 2022). Some characteristics and examples are that it is highly related to data science and uses many technologies and techniques, from traditional data warehouses to modern approaches like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
What are Business Intelligence and its benefits?
On the other hand, a business intelligence implementation or solution offers a system comprised of descriptive analytics and quantitative and qualitative information to support business users’ decision-making by transforming data into valuable insights in the present state. This data set is commonly presented in a dashboard format like graphs, maps, and charts with detailed intelligence regarding the business (Olavsrud & Fruhlinger, 2023). Some examples of this Business Intelligence software are Tableau, Qlik, and Microsoft Power BI.
This solution has the ability, strength, and adaptability to provide business computing insights that could improve overall organizational performance and profitability. (Levin, 2017). The attributes of business intelligence are relevancy, accuracy, and accessibility.
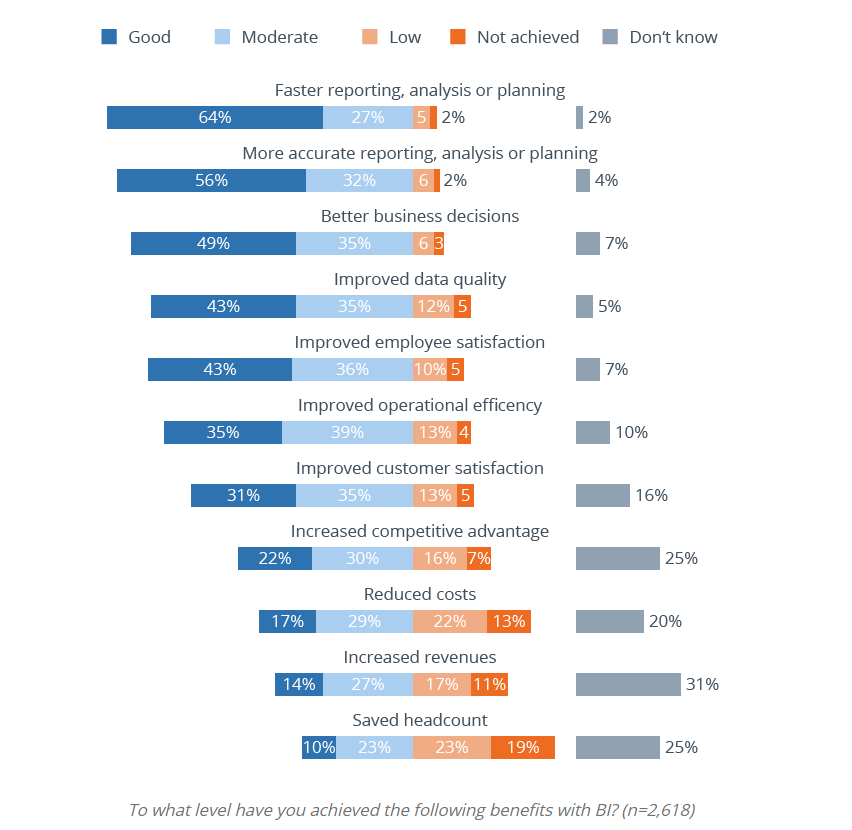
The benefits of BI include and are not limited to the following (BI-Survey.com, n.d.):
- The speed and accuracy of analysis and reporting to support business decisions that result in higher returns and profitability.
- Improved data quality, workflow efficiency, and employee and customer satisfaction will help boost the business’s brand and overall quality.
- Ability to reduce costs while growing revenues with data integration and automation.
- It increases competitiveness.
An Overview of Business Intelligence Process
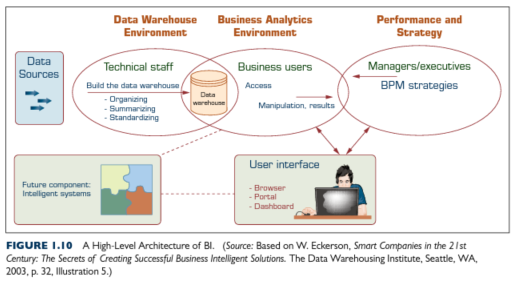
A Business Intelligence system has four major components for consideration:
- A Data Warehouse; is a centralised repository of information connected or integrated with one or more data sources.
- Business Analytics; is a collection of tools used for processing the data in the Data Warehouse, including Data Mining, manipulating, and analysing data.
- Business Performance Management (BPM); BPM is being used for monitoring and analyzing organisation’s performance to achieve its goal.
- A user interface; is the output of information presented in a particular format, usually in dashboards or interactive reports to business users.
How can business get started: From the System Design to System Acquisition
A system design seeks to offer a high-quality information system that meets business needs and enhances current business procedures to increase the system’s efficiency as a whole. The qualities of the data, including its reliability as a source, its accuracy as material, its security, its consistency, and its readiness level, are crucial to determining its quality. (Sharda, Delen, Turban & King, 2014).
The creation of a data warehouse or DM (Data Mart), which allows quicker results because DMs are less complex than EDW, is the logical system design (Entity-Relationship model) to adopt when pioneering with a bottom-up approach via a Kimball Model. (Enterprise Data Warehouse). Due to its lower costs and better success rates, this strategy is popular. (Rangarajan, 2016). This method is also the best and most efficient way to adapt it to a test run and serve as a “proof of concept” application before starting a full-scale EDW project.
It will be advantageous to acquire a customized off-the-shelf leading tool/solution or Software as a Service (SaaS) like Microsoft Power BI, Qlik, and Tableau that can be tailored to the requirements of each business unit (Olavsrud & Fruhlinger, 2023). This approach also supports scaling upwards efficiently to even more data sources and enables integration to accommodate the organisation’s needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting business intelligence is the first step towards big data analytics to support a business need, despite the organisation’s size. This approach is obviously a desirable option for SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) to benefit from. The benefits and returns of its adoption are significant, with scalability potential. This technology is vital to strengthen the business towards big data analytics as the business’s data is not limited to its primary (internal) sources but also accessible to secondary (external) through multiple sources of business and digital platforms that could aid in making an informed business decision and improve overall customer’s experience (Tran, 2022).
References:
BI-Survey.com. (n.d.). BI Tools Need to Turn Data into Insights and Action. Retrieved 15 March, 2023, from https://bi-survey.com/benefits-business-intelligence
Olavsrud. T. and Fruhlinger. J. (2023, January 20). What is business intelligence? Transforming data into business insights. CIO. Retrieved 15 March, 2023, from https://www.cio.com/article/2439504/business-intelligence/business-intelligence-definition-and-solutions.html
Levin. N. (2017, January 14). Microsoft Power BI for Retail and eCommerce. LinkedIn Article. Retrieved 15 Mar, 2023 from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/microsoft-power-bi-retail-ecommerce-neal-levin/
Rangarajan. S. (2016, September 1). Data Warehouse Design – Inmon versus Kimball. The Data Administration Newsletter. Retrieved 15 March, 2023, from http://tdan.com/data-warehouse-design-inmon-versus-kimball/20300
Sharda. R., Delen. D., Turban. E. and King. D. (2014). An Overview of Business Intelligence, Analytics, and Decision Support. Business Intelligence: A managerial perspective on analytics. Third Edition. Pp. 34-40.
Sturdy. G.R. (2012). Chapter 8: Business Intelligence, Business Intelligence Description. Customer Relationship Management using Business Intelligence. Pp. 149-153.
Tran. T. (2022, August 11). Big Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: What’re the discrepancies? Orient. Retrieved 17 March, 2023, from https://www.orientsoftware.com/blog/big-data-analytics-and-business-intelligence/